Top 10 Warehouse Automation Robots Transforming Supply Chain Efficiency
In the rapidly evolving landscape of logistics and supply chain management, the adoption of warehouse automation robots has emerged as a game-changing strategy for enhancing operational efficiency. According to a report by Allied Market Research, the global warehouse automation market is projected to reach $30 billion by 2026, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.9% from 2019 to 2026. This meteoric rise is driven by an increasing need for streamlined operations, reduced labor costs, and heightened demand for faster delivery times, particularly as e-commerce continues to expand.
Warehouse automation robots play a crucial role in addressing these challenges by optimizing various processes, such as inventory management, order fulfillment, and transportation within warehouses. A study conducted by McKinsey & Company highlights that automation can boost overall productivity by 30% to 50%, significantly reducing the time required for tasks traditionally handled by human labor. The integration of robotics not only alleviates the burdens of repetitive tasks but also enhances accuracy and safety in warehouse environments. As organizations seek to stay competitive in a demanding market, understanding the top warehouse automation robots transforming supply chain efficiency will be essential in harnessing the full potential of this technological advancement.

Overview of Warehouse Automation and Its Importance
Warehouse automation has become a cornerstone of modern supply chain management, revolutionizing how goods are handled and distributed. In today’s fast-paced environment, efficiency is paramount, and the integration of automation technologies allows warehouses to operate with unprecedented speed and accuracy. These automated systems not only streamline operations but also reduce human error, optimize inventory management, and enhance overall productivity. As businesses face growing consumer demands and the complexities of global logistics, warehouse automation emerges as a vital solution, ensuring that operations remain agile and responsive.
When considering the implementation of warehouse automation, it's crucial to assess your specific needs and capabilities. Start by analyzing current workflows to identify bottlenecks where automation can have the most impact. Engaging with employees during this process can provide insights into practical challenges and help tailor solutions that complement existing operations.
Moreover, investing in employee training is key to successful automation. Ensuring that staff are equipped with the knowledge and skills to operate and maintain automated systems will not only boost efficiency but also foster a collaborative working environment. With proper planning and execution, the transition to a more automated warehouse can lead to significant improvements in supply chain performance.
Key Benefits of Implementing Automation in Supply Chains
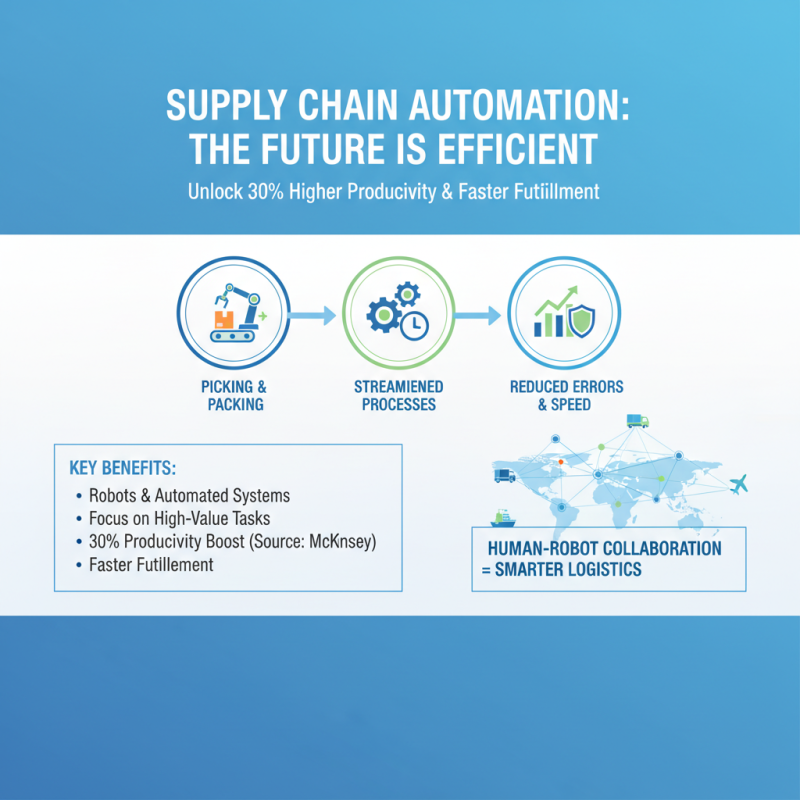
In the fast-evolving landscape of supply chain management, automation has emerged as a transformative force, significantly enhancing operational efficiency. According to a recent report by McKinsey, the integration of automation technologies can improve warehouse productivity by as much as 30%. This optimization is largely due to robots and automated systems performing repetitive tasks and streamlining processes, which allows human workers to focus on higher-value activities. By automating routine functions like picking, packing, and sorting, companies can drastically reduce errors and improve fulfillment speed.
Implementing warehouse automation not only boosts productivity but also enhances inventory management. A study from the Harvard Business Review indicates that firms utilizing automated inventory systems can reduce their inventory costs by up to 25%, thanks to real-time data analytics and precise tracking capabilities. This shift leads to better decision-making and less waste, which are critical in today’s competitive market.
Tip: When considering automation, assess your specific operational needs and start with pilot projects to evaluate impact before widespread implementation. Additionally, invest in employee training to ensure a seamless transition and maximize the benefits of the new technology. Fostering a culture that embraces automation will enhance collaboration between human workers and robots, driving overall supply chain efficiency.
Types of Robots Used in Warehouse Automation
Warehouse automation is revolutionizing supply chain management by significantly enhancing efficiency and accuracy. Various types of robots play a crucial role in automating tasks traditionally performed by human workers, with significant impacts on productivity. According to a report from Research and Markets, the global warehouse automation market is projected to reach USD 27.2 billion by 2026, growing at a CAGR of 14.7%. This growth is driven primarily by the increased use of robotics in warehouses, which helps in reducing operational costs and improving order fulfillment times.
One of the most prevalent types of robots in warehouse automation is Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs), which navigate using sophisticated sensors and software to transport goods within the facility. These robots are designed to work collaboratively with existing human workflows, enhancing the speed and safety of operations. Additionally, Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) are widely used for repetitive tasks such as pallet transport and sorting, minimizing manual errors and increasing throughput. According to a McKinsey report, warehouses utilizing robotics can increase productivity levels by up to 30%, showcasing the transformative potential of these technologies in modern supply chain environments.
Moreover, robotic arms are gaining traction in activities such as picking and packing, significantly reducing the time it takes to assemble orders. As automation becomes more integrated with artificial intelligence and machine learning, warehouses will see even greater levels of customization and speed in their operations. According to a report by the International Federation of Robotics, the density of industrial robots in warehouses is expected to increase by 40% over the next five years. This shift signals a substantial move towards fully automated supply chain solutions that not only elevate operational efficiency but also enhance overall service delivery.
Top 10 Warehouse Automation Robots and Their Features
Warehouse automation robots are revolutionizing the supply chain landscape by enhancing efficiency and productivity. These robots come equipped with a variety of features tailored to streamline warehouse operations. One of the most significant features is their ability to navigate autonomously through complex environments. This capability allows them to transport goods with precision, reducing the potential for human error and speeding up order fulfillment processes. Additionally, many models are designed with advanced sensors and cameras that enable real-time inventory tracking and monitoring, providing warehouses with accurate data to optimize stock levels.
Another notable feature of these robots is their versatility in handling various tasks. Some are equipped for picking and sorting items, while others are designed for palletizing and loading. This multi-functionality means that a single robot can perform several tasks, thus minimizing the need for multiple different machines and lowering operational costs. Moreover, many warehouse automation robots are integrated with artificial intelligence and machine learning, allowing them to learn from their surroundings and improve their performance over time. This intelligent adaptability is crucial for meeting the demands of modern supply chains, where efficiency and speed are paramount for success.
Future Trends in Warehouse Automation Technology
The landscape of warehouse automation is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and the increasing demand for efficiency in supply chains. According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets, the warehouse automation market is projected to grow from $15.7 billion in 2023 to $37.4 billion by 2030, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.2%. This growth underscores the critical role that automation plays in enhancing productivity, reducing labor costs, and improving inventory management.
One of the key trends shaping the future of warehouse automation is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms. These technologies enable robots to optimize their operations through real-time data analysis, allowing for smarter decision-making in picking, packing, and sorting processes. Additionally, the implementation of autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) is on the rise, as they provide greater flexibility in navigating complex warehouse environments, significantly speeding up order fulfillment rates. According to a report by the International Federation of Robotics, the global stock of operational warehouse robots is set to exceed 4 million units by 2025, highlighting the accelerating shift toward automated solutions.
Furthermore, advancements in robotics are not just limited to movement; collaborative robots, or cobots, are being developed to work alongside human operators, enhancing the flexibility and safety of warehouse environments. Data from the Robotics Business Review indicates that cobot sales are expected to rise by over 30% annually, as companies look to blend human dexterity with robotic efficiency. This trend signifies a shift toward a more collaborative approach in warehouse operations, promising to transform supply chain efficiency even further while addressing labor shortages and increasing operational demand.
Top 10 Warehouse Automation Robots Transforming Supply Chain Efficiency
| Robot Model | Type | Key Features | Average Speed (m/s) | Payload Capacity (kg) | Integration Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model A | Autonomous Mobile Robot (AMR) | Navigation & Mapping, Obstacle Avoidance | 1.5 | 150 | High |
| Model B | Automated Guided Vehicle (AGV) | Route Optimization, Docking | 1.0 | 250 | Medium |
| Model C | Pick-and-Place Robot | High Precision, Rapid Movement | 2.0 | 50 | High |
| Model D | Sorting Robot | Batch Sorting, AI Learning | 1.8 | 100 | High |
| Model E | Collaborative Robot (Cobot) | Safety Sensors, Human Interaction | 1.2 | 20 | Very High |
| Model F | Warehouse Drone | Inventory Tracking, Aerial View | 3.0 | 10 | Medium |
| Model G | Gantry Robot | Heavy Lifting, High Speed | 1.6 | 500 | High |
| Model H | Conveyor Robot | Continuous Flow, Integration Flexibility | 2.5 | 200 | High |
| Model I | Shrink Wrapper Robot | Wrap Automation, Space Saving | 1.2 | 150 | Medium |
| Model J | Palletizing Robot | Stacking Efficiency, High Throughput | 1.6 | 300 | High |
Related Posts
-

2025 Top 5 Picking Robots for Efficient Agricultural Automation
-

Top 10 Robotic Process Automation Software Options You Should Know About
-

Exploring the Future of Robotics Engineering in Everyday Life
-
10 Tips for Choosing the Right Industrial Robotic Arm for Your Business
-
Top 5 Robotics Companies Driving $110 Billion Global Market Growth in 2023
-

Top 10 Robotics Companies Leading the Future of Automation and Innovation
Smart Robotics brand movie
Watch video


