2026 How to Use a Robotic Arm for Automation in Various Industries?
In recent years, the adoption of robotic arms in various industries has surged. According to a 2022 report by the International Federation of Robotics, global sales of robotic arms grew by 16% year-on-year. These advanced machines transform production lines, enhancing precision and efficiency. Manufacturers across sectors are turning to robotic arms to meet rising consumer demands.
Robotic arms are utilized in automotive, electronics, and healthcare industries. In automotive manufacturing, they handle assembly tasks and paint jobs. This reduces errors and accelerates output. However, many businesses still hesitate to implement these technologies. Concerns about initial costs and job displacement loom large.
Despite these challenges, the benefits are compelling. For instance, a study by McKinsey found that automation can increase productivity by up to 30%. It is vital for businesses to assess their operational needs. Embracing robotic arms could provide a competitive edge. Yet, the journey toward automation requires careful planning and reflection on the long-term impact.

Understanding Robotic Arms: Definition and Components
Robotic arms are revolutionary tools in many industries. They are essentially mechanical arms designed to perform tasks automatically. Understanding their components is essential for effective use. Each robotic arm consists of joints, links, and an end effector. Joints allow movement, while links connect these joints. The end effector is the part that interacts with the environment.
These arms can be complex and require careful consideration. Not every design fits every need. For instance, a simple assembly line may only need a few basic movements. In contrast, a manufacturing plant may require intricate movements for precise assembly. Sometimes, selecting the right components can be overwhelming, especially for beginners. Testing different configurations is often necessary, leading to trial and error.
Components of robotic arms also face limitations. For example, motors may wear out over time, affecting performance. Regular maintenance is crucial but often overlooked. The programming aspect can also prove challenging. Ensuring the robotic arm communicates effectively with software requires understanding both hardware and programming logic. Miscommunication can lead to errors. So, while robotic arms hold great potential, careful planning and consideration are key to their successful integration.
Types of Robotic Arms Used in Industrial Automation
In industrial automation, various types of robotic arms play crucial roles. Articulated arms, with multiple joints, are ideal for tasks requiring flexibility. They excel in assembly lines and complex operations. In fact, studies show that articulated robots can improve production rates by up to 30%.
Another popular type is SCARA robots. They are known for high-speed pick-and-place tasks. Their design allows for quick lateral movements. SCARA arms are often used in manufacturing electronics, where precision is key. Reports indicate that this speed can boost throughput by nearly 50%.
Tips: When choosing a robotic arm, consider its workload capacity and range of motion. Ensure it fits seamlessly into your current workflow. Also, investing in training can maximize efficiency.
Collaborative robots, or cobots, are gaining traction too. They are designed to work alongside human workers. Cobots enhance productivity without replacing the workforce. However, the integration process can be challenging. Companies must be mindful of safety standards and operational limits.
Understanding these robot types helps industries adopt automation effectively. Evaluate your specific needs before deployment. Each type has unique benefits and limitations worth exploring.
2026 How to Use a Robotic Arm for Automation in Various Industries?
| Type of Robotic Arm | Applications | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Articulated Robots | Welding, Painting, Assembly | High flexibility and reach | Complex programming |
| SCARA Robots | Pick and Place, Assembly | Rapid operation and high precision | Limited vertical reach |
| Delta Robots | Food Packaging, Electronics Handling | Extremely fast and lightweight | Limited payload capacity |
| Cartesian Robots | 3D Printing, CNC Machining | Simplicity and ease of programming | Limited to Cartesian coordinates |
| Collaborative Robots (Cobots) | Assembly, Quality Inspection | Safe interaction with humans | Lower payload capacity |
Applications of Robotic Arms in Manufacturing Processes
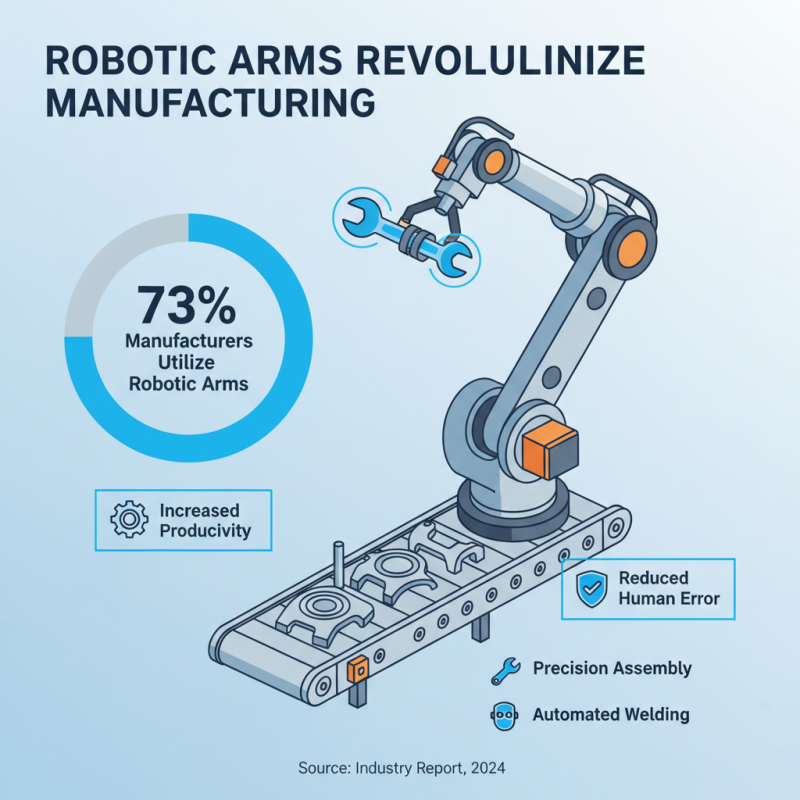
Robotic arms have transformed manufacturing processes drastically. They are designed to perform specific tasks with high precision, speed, and reliability. According to a recent industry report, 73% of manufacturers now utilize robotic arms in their operations. These machines excel in repetitive tasks, like assembly and welding, which improves productivity and reduces human error.
In automotive production, robotic arms are particularly influential. They handle tasks such as painting and assembling vehicle parts. Data shows that the use of robotic arms can increase production rates by up to 30%. However, the integration isn't without challenges. Many companies encounter difficulties in programming and maintaining these systems. Additionally, workers often need retraining, which can disrupt workflow temporarily.
The food and beverage sector also benefits from robotic arms. They assist in packaging and sorting products efficiently. A notable statistic indicates that automation here can reduce costs by 20%. Nevertheless, industries must consider the balance between automation and job displacement. Investing in robotic arms requires careful planning to address these concerns while harnessing their potential.
Challenges and Solutions in Implementing Robotic Arms
Implementing robotic arms in various industries brings unique challenges. One major issue is the high initial investment. Companies may hesitate due to the cost of purchasing and integrating these systems. It is crucial to thoroughly analyze the potential return on investment. If the calculations are wrong, companies risk financial loss.
Another challenge is training the workforce. Employees may feel threatened by automation. They might resist learning new skills required to work alongside robots. Proper training programs must address these fears. Encouraging collaboration between humans and robots can build a more cohesive work environment.
Integration with existing systems is also complex. Robotic arms need to communicate with other machinery seamlessly. Often, existing systems are outdated or incompatible. This gap can lead to inefficiencies. Investing time in troubleshooting and system upgrades is essential for success. Without coordination, the benefits of automation can quickly diminish.
Robotic Arm Adoption Rates by Industry in 2026
Future Trends in Robotic Arm Technology for Automation
In the world of automation, robotic arms are transforming industries. Their ability to perform repetitive tasks efficiently is invaluable. As we look toward 2026, several trends are emerging. Enhanced AI integration is allowing robotic arms to learn. This adaptability enables them to make real-time adjustments, increasing overall productivity.
Another exciting development is the miniaturization of robotic arms. Smaller devices can work in tighter spaces. They’re becoming crucial in sectors like healthcare and electronics. However, the cost of advanced technology raises questions. Smaller companies may struggle to keep up. This disparity could limit the benefits of automation.
Collaboration between humans and robots is also on the rise. Newer robotic arms can work alongside workers. They tackle heavy lifting while humans focus on more complex tasks. Still, challenges arise in safety and job displacement. Training workers to interact with robots is essential. Balancing innovation with social responsibility requires ongoing dialogue.
Related Posts
-

Top 10 Robotic Arm Applications Transforming Industries You Must Know
-
10 Tips for Choosing the Right Industrial Robotic Arm for Your Business
-
How to Enhance Manufacturing Efficiency with Cobot Robots in Your Business
-

What Are the Advantages of Using Robotic Process Automation Tools
-

10 Proven Benefits of Robotic Process Automation Software for Boosting Business Efficiency
-

What is a Packaging Robot and How It Revolutionizes the Packaging Industry
Smart Robotics brand movie
Watch video


