10 Essential Tips for Mastering Robotics and Automation Techniques?
In today's ever-evolving landscape, mastering robotics and automation is crucial. As Dr. Sarah Johnson, a leading expert in the field, stated, "Robotics and automation hold the power to redefine industries." This is evident in sectors like manufacturing and healthcare, where efficiency has skyrocketed.
However, diving into robotics and automation is not without challenges. Enthusiasts often overlook the importance of hands-on experience. Understanding coding languages and the mechanics of machines is essential, yet many attempt this journey without foundational knowledge. This can lead to frustration and setbacks.
Moreover, creativity plays a vital role. It is not enough to follow guidelines and replicate existing models. Innovating within the constraints can spark remarkable solutions. In this pursuit, learners must embrace failures as stepping stones to success. The path to mastering robotics and automation includes a blend of trial and error, continuous learning, and adaptation.

Understanding the Basics of Robotics and Automation Systems
Robotics and automation systems are becoming essential in various industries. These technologies streamline processes, reduce labor costs, and improve efficiency. According to a report by McKinsey, automation could increase global productivity by up to 1.4% annually. This shift demands a solid understanding of key concepts, allowing professionals to adapt and excel.
Basic robotics involves sensors, actuators, and controllers. Sensors gather data about the environment. Actuators convert this data into actions. Controllers serve as the brain of the operation, making decisions based on incoming data. Mastering these components is crucial. Yet, many overlook their importance. The lack of hands-on experience in these areas often hinders effective application.
Meanwhile, automation systems rely on software algorithms and machine learning. These tools analyze data and improve operations over time. It's easy to see the benefits. However, the integration of these systems can pose challenges. Companies often face resistance to change. Employees may fear job displacement, which complicates adoption. Addressing these concerns is vital for smooth transitions in any robotic or automated setup.
Understanding Robotics and Automation Techniques
This chart displays the growth in the number of robotics and automation systems implemented across different industries over the past five years. The data reflects industries moving towards automation to enhance efficiency and productivity.
Exploring Common Robotics Technologies and Their Applications
Robotics technology is transforming various industries today. From manufacturing to healthcare, robots enhance efficiency and precision. According to a report by McKinsey, automation could increase global productivity by up to 1.4% annually. This shift signifies a need for skilled individuals who understand these technologies.
Common robotics technologies include industrial robots, drones, and collaborative robots (cobots). Industrial robots automate tasks on assembly lines. They can work tirelessly, performing repetitive tasks with high accuracy. Drones are used for delivery, surveillance, and agriculture. Cobots work alongside humans, assisting in tasks without replacing them. A study from PwC predicts that by 2030, automation could displace around 20 million manufacturing jobs. However, this also creates new opportunities for skilled labor in programming and maintenance.
Despite these advancements, challenges persist. Integration of robotics into existing systems can be complex. Training employees to work with new technologies is essential. Many companies struggle to update their workforce's skills effectively. Robotics presents clear benefits, but the pathway to mastery requires reflection and adaptation.
10 Essential Tips for Mastering Robotics and Automation Techniques
| Tip No. | Tip Description | Common Technologies | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Understand the fundamentals of mechanics. | Kinematics, Dynamics | Robotic arms, Automated manufacturing |
| 2 | Learn programming languages relevant to robotics. | Python, C++, ROS | Robot control, Simulation |
| 3 | Experiment with different sensors and actuators. | Infrared, Ultrasonic, Motors | Obstacle detection, Motion control |
| 4 | Study automation processes and control theory. | PID Control, Fuzzy Logic | Industrial automation, Robotics |
| 5 | Practice building small projects. | DIY kits, Arduino | Educational robots, Prototyping |
| 6 | Collaborate with others on robotics projects. | Robotics clubs, Hackathons | Team-based innovation, Skills development |
| 7 | Stay updated with the latest trends in robot technology. | AI, Machine Learning | Autonomous systems, Smart robots |
| 8 | Engage in competitions to apply skills. | Robotics competitions, Challenges | Performance evaluation, Skill enhancement |
| 9 | Utilize simulation software for better design. | Gazebo, V-REP | Model testing, Scenario planning |
| 10 | Document your learning journey and projects. | Blogs, Video tutorials | Knowledge sharing, Portfolio development |
Essential Programming Languages for Robotics Development
When diving into robotics, programming languages are your best friends. Knowing the right languages can reshape your projects. Python, for instance, is popular due to its simplicity and efficiency. You can quickly prototype ideas with fewer lines of code. It’s user-friendly, making it suitable for beginners. But don’t rely solely on it. As you progress, you might need more robust languages.
C++ holds a significant place in robotics. Its performance and control over hardware are unmatched. Many robots require precision and speed, which C++ excels at providing. However, it also comes with a steep learning curve. You may find yourself frustrated while writing complex code. Yet, persistence is key. Understanding C++ can unlock advanced capabilities for your projects.
Another language worth considering is ROS. It’s not a programming language in the traditional sense. Instead, it’s a framework that helps manage robotics applications. Learning ROS can dramatically enhance your efficiency. You will face challenges, especially if you try to solve everything at once. Break tasks down, and embrace the learning process. Cultivating these skills can significantly strengthen your robotics toolkit.
Best Practices for Designing and Building Automated Systems
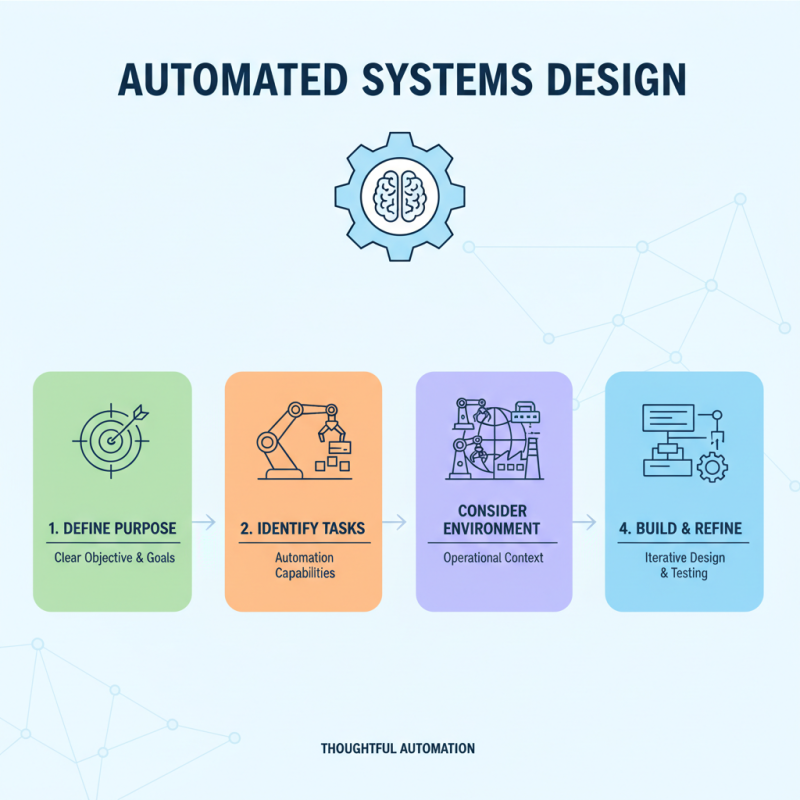
Designing and building automated systems requires a thoughtful approach. Begin by defining the purpose of your robotic system. A clear objective helps guide your design choices. Identify the tasks you want the automation to perform. Consider the environment in which the robots will operate. This can significantly affect functionality.
Select appropriate sensors and actuators for your system. These components are critical to achieving accuracy. Make sure you understand their limitations. For example, vision systems may struggle in low-light conditions. Ensure your design accommodates potential failures. Redundancy can provide backup when a component fails.
Testing is vital in the development process. Create scenarios to evaluate system performance. This helps uncover areas needing improvement. Don’t hesitate to iterate on your design. Each version should address previous shortcomings. Learning from mistakes is part of mastering automation techniques.
Staying Updated: Resources for Advancing in Robotics and Automation
In the fast-evolving field of robotics and automation, staying updated is vital. According to a report from the International Federation of Robotics, the industrial robot market is expected to grow by 10% annually through 2025. This growth suggests that professionals must constantly refine their skills. Online courses, webinars, and local workshops offer great opportunities for education. However, finding the right resource can be overwhelming. Filtering through endless options requires patience and discernment.
Industry reports indicate that nearly 58% of professionals feel unprepared for advancements in technology. This gap highlights the importance of continuous learning. For instance, platforms like MOOCs provide access to resources from top universities. Engaging with community forums can also enhance learning. But, it's crucial to participate actively rather than consume passively. Many overlook hands-on practice, which is key for mastering automation techniques.
Keeping up with journals and industry publications helps maintain awareness of trends. Some argue that focusing solely on big trends leaves gaps in fundamental knowledge. Reflection on personal goals and challenges is essential for improvement. Balancing theoretical knowledge with practical applications can be difficult, yet it is necessary for growth in this dynamic field.
Related Posts
-

Top Robotic Solutions to Transform Your Business in 2025
-
How to Enhance Manufacturing Efficiency with Cobot Robots in Your Business
-

The Future of Work How Industrial Robots are Transforming Manufacturing Industries
-
Unlocking the Future of Work with Robotic Process Automation for Everyday Tasks
-

Exploring the Future of Robotics Engineering in Everyday Life
-

Revolutionizing Supply Chains: How Warehouse Robots Are Shaping the Future of Logistics
Smart Robotics brand movie
Watch video


